

While pharmacists often monitor their patients’ INRs, it is usually doctors who manage patients who have become over- anticoagulated. They are also used to treat current DVTs or pulmonary emboli.Īppropriate management of warfarin therapy requires monitoring of patients’ international normalised ratios (INRs). They are used for several indications, including thromboprophylaxis for patients with atrial fibrillation, or who have undergone a mechanical heart valve replacement or had deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Oral vitamin K antagonist anticoagulants (eg, warfarin sodium) are prescribed for around 500,000 patients in the UK at any one time 1.

We do not recommend that you take any clinical decisions based on this information without first ensuring you have checked the latest guidance.
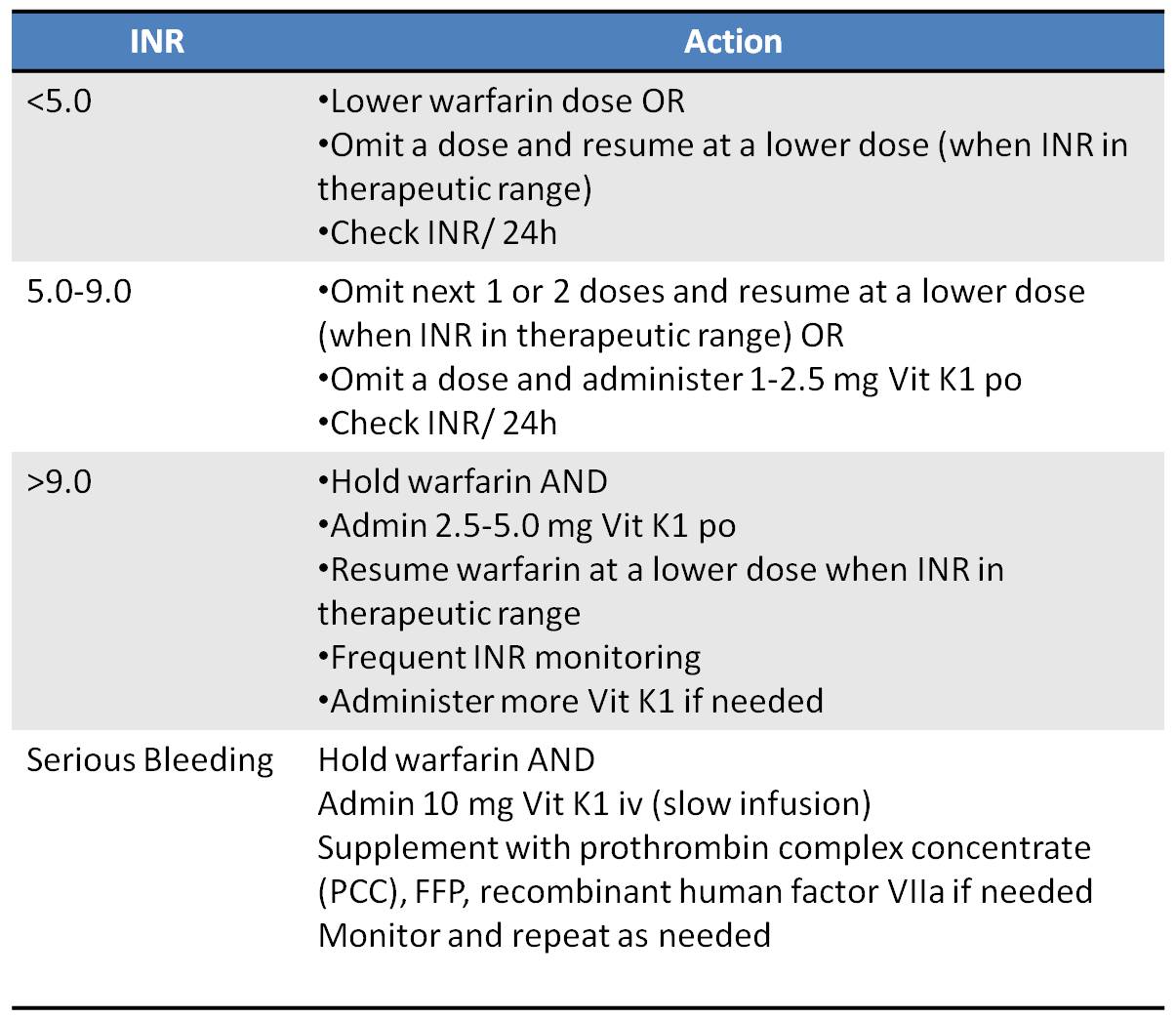
Serious bleeding manifestations are common.

Severe deficiency of vitamin K–dependent proteins in patients not maintained on vitamin K antagonists is most commonly associated with poisoning by or surreptitious ingestion of warfarin, warfarin-like anticoagulants, or potent rodenticides (“superwarfarins”), such as brodifacoum.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
